Update on Oct. 29th, 2018. Keyword research is a foundational tactic that sets the stage for your entire SEO campaign. Because of this, it is vital that you do your due diligence and use all of the tools available to ensure you uncover all of the best opportunities to pursue. In today’s post, I am going to talk about two different tools and how to use them to uncover great keyword opportunities for your business. We will be talking about Google Trends and the Google Keyword Planner.
Understanding Demand Through Google Trends
Google trends can help you better understand what the demand is for keywords related to your website and products. Based on trends, it can also predict what demand might be in the future and if certain keywords have seasonal or geographic popularity. Knowing what the demand is for your product (not just WHAT people are searching but also WHEN and WHERE) can help you better target potential customers and drive more valuable traffic to your web pages.Keyword demand by region
Did you know you can use Google Trends to see what people are searching in specific regions? By looking to see where your product (or keywords related to your product) are being searched, you can determine where your products or services are needed most. Say you sell rain boots. Your product is, generally, more relevant to people who live in rainy regions, right? But do you know what cities and subregions have the highest searches for rain boots? To get that data, you can enter keywords into Google Trends and then view “Interest by Subregion.” Using the keyword groups/themes you just built, take the first five keywords found in each keyword theme and add them to the tool, then scroll down to “Interest by Subregion” in order to view the country, state, or city where your keywords (and related keywords) are searched the most.


How to use this Google Trend keyword data strategically
- Save money on Pay-Per-Click Ads (Google Adwords) by targeting regions with the most demand. This data can help you increase your ROI, since you’ll know you need to be targeting rain boot ads to folks in New York, Mississippi, Washington, and more.
- Leverage regional trends with useful content for those areas. If you already know a huge majority of people searching for “rain boots” are in Portland, you can create Portland-specific content for your website. This can help you bring in more relevant potential customers through organic search and retarget those visitors via paid social media ads.

Example: How to Survive Portland’s Rainy Season
Keyword demand over time (search trends)
What you will see next is the search demand, charted from month to month over the last few years. You will be able to clearly see if certain keywords are decreasing in demand and others are increasing in demand. In the example below, you can clearly see that the keyword ‘Rain boots’ is continuing to gain popularity after July whereas the keyword ‘s “Water boot’ is staying consistent in popularity. Once you have this data, you can make educated decisions on which keywords you should put most of your effort towards, since you’ll know what searches are trending up and what searches are trending down. However, don’t give up completely on keywords that are declining — there will still be searches performed and visitors to capture (and potentially less competition for those keywords). But because you know they’re trending downward in popularity, you need to figure out how to prioritize them with more important terms trending upwards. This is where Google’s keyword planner is critical to use so you have a secondary data source for additional insights.
Once you have this data, you can make educated decisions on which keywords you should put most of your effort towards, since you’ll know what searches are trending up and what searches are trending down. However, don’t give up completely on keywords that are declining — there will still be searches performed and visitors to capture (and potentially less competition for those keywords). But because you know they’re trending downward in popularity, you need to figure out how to prioritize them with more important terms trending upwards. This is where Google’s keyword planner is critical to use so you have a secondary data source for additional insights. Keyword Discovery Through The Google Keyword Planner
To find the very best keywords for your web pages, you should start by doing some basic keyword research with the Google Keyword Planner Tool. You’ll start by inserting one keyword you consider to be related to your business or product into the tool and select your settings. The settings we always use are the default settings, except for changing the match types from broadly related ideas to closely related ideas. This helps us find more specific keywords that match the search intent we’re looking for. You will want to change other settings if you are targeting individuals in different geographic locations or across different devices. After you have tweaked your settings, click ‘search’ and you will be shown a list of keywords related to your initial search, including how many global and local searches were performed last month for these keywords. Please note that the search volume listed in this tool is not always accurate. Take these numbers as more of a rough estimate and use them more as a comparison across different keywords to determine which are more popular than others. For a specific example, if we take the keywords above (rain boots) and search in a specific area like New York, you will see how search volume adjusts. Compare that with a broader search in the U.S. will show you the difference in search volume.
You will want to change other settings if you are targeting individuals in different geographic locations or across different devices. After you have tweaked your settings, click ‘search’ and you will be shown a list of keywords related to your initial search, including how many global and local searches were performed last month for these keywords. Please note that the search volume listed in this tool is not always accurate. Take these numbers as more of a rough estimate and use them more as a comparison across different keywords to determine which are more popular than others. For a specific example, if we take the keywords above (rain boots) and search in a specific area like New York, you will see how search volume adjusts. Compare that with a broader search in the U.S. will show you the difference in search volume. 

Grouping Keywords Together Into Related Themes
The next step in the process is to take the keywords you generated in the Keyword Tool and group them into closely related groups or themes. For example, if I were doing keyword research for a shoe company, the words cheap rain boots, rain boots deal, and other closely related keywords would be in the same group. The words rain boots for women, women’s tall rain boots, and women’s rubber rain boots would be in another group. We’ll cover this in more depth below but this is a basic example for now.Why group keywords together
Grouping keywords together into related themes will help you build more natural SEO value into each page while helping you stay organized and track your ranking improvements. Because Google will crawl your page to determine its relevance to a given topic, having closely-related keywords on specific pages will help Google better understand your page is relevant. Using closely-related but not identical keywords over and over will also prevent you from over-optimizing a page. Google’s Panda updates are aimed at punishing sites which have over-optimized content. If you have pages that are over optimized, you may see a sudden drop in keyword rankings. This will also keep you from cannibalizing keywords across multiple pages of your site if you have closely related pages, which happens a lot for eCommerce sites.Group keywords together that answer the same question
If you have multiple keywords that are clearly asking the same question (or looking for the same result) then those keywords should be placed together in the same category. For example, “rain boots,” “waterproof boots,” and “rubber boots,” are all very different keywords, but have the same search intent. If you sell rain boots, all three keywords should be grouped together and mapped to the most relevant page on your site such as the homepage or main boots page, depending on how the site is structured. If you have a separate page specifically for women’s rain boots, group together keywords related specifically to that search intent. “Women’s rain boots,” “rain boots for women,” “women’s short rain boots,” and “women’s low rain boots,” are all real search queries that your page could relevantly answer. Later in the post, we’ll go over how to use keyword groupings to build “themes” for each page, so you can effectively communicate to Google the purpose and subject matter of each of your pages, earning you increased visibility in search results.Map Keywords To Individual Pages
After you’ve built distinct groupings for your keywords, your next step is to take your keyword groups and map them to individual pages on your website.What is keyword mapping?
Keyword mapping is the practice of pairing relevant keyword groupings with the correct pages on your website. Determining exactly what keywords are relevant to each page is a major part of on-page SEO, as it helps Google see the relevance between your page and those search queries, ranking your pages higher. The engines start to get confused when the same keyword themes are mapped to more than one page, so make sure you have just one page per keyword theme. This is why grouping your keywords is so important.How many keywords or keyword groups should you map to one page?
A general rule of thumb is to assign 3 to 5 terms per page. This may vary depending on how much copy you can put on each page, while still having the copy seem natural and closely related to the terms you are targeting. You may be tempted to try and get pages to rank for as many terms as possible, but this can confuse google about what information is truly relevant on your page. Even if you branch out to include long-tail keywords and other search queries on your page, make sure every keyword has the same answer (and that the answer is YOUR PAGE!)How to make a keyword map
1. Identify the keywords and keyword groupings your site SHOULD be ranking for Your goal should be to create a list of keywords your site should be ranking for. The more relevant keywords, the better: Think outside your own website structure, and beyond the keywords, you’re already ranking for. Consider the keywords your competitors are currently ranking for, and how they are using them on each page in the content, title tag, header tags, alt text for images, meta description tag, etc. Then work to include them on each page. Leveraging tools like the keyword planner in addition to Google search can be extremely useful in planning your keyword strategy. For example, if you were a discount shoe store, you may want to compare yourself to Zulily. When we search on google typing “site:zulily.com rain boots” we are able to see other keywords they are targeting. Next, we can use these keywords in keyword planner to see if they are terms we should also be using. Based on their keywords and their average search volume, you could use keywords like “toddler rain boots,” “kids rain boots,” “tall rain boots for kids,” and many others. While the keyword “colorful and patterned rain boots” may not be the best idea since there is no search volume for that phrase, you could use the keyword planner and look into other terms that include colorful or patterned.
Next, we can use these keywords in keyword planner to see if they are terms we should also be using. Based on their keywords and their average search volume, you could use keywords like “toddler rain boots,” “kids rain boots,” “tall rain boots for kids,” and many others. While the keyword “colorful and patterned rain boots” may not be the best idea since there is no search volume for that phrase, you could use the keyword planner and look into other terms that include colorful or patterned. 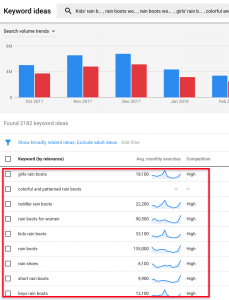 Earlier, you created keyword groupings using the Google Keyword tool. Now, we’ll begin assigning them to relevant URLs on your site. 2. Build out your site structure and URLs based on your keyword map You can use your newly-created keyword groupings to visualize potential pages as part of your site structure, helping you create a user-friendly, search-friendly path through your website for visitors.
Earlier, you created keyword groupings using the Google Keyword tool. Now, we’ll begin assigning them to relevant URLs on your site. 2. Build out your site structure and URLs based on your keyword map You can use your newly-created keyword groupings to visualize potential pages as part of your site structure, helping you create a user-friendly, search-friendly path through your website for visitors.  Keyword mapping like this can help you think of every page on your site in terms of “themes.” If you see a theme in your keyword map that does not yet have a URL, you can consider creating a new URL for it. By leveraging these powerful keyword research strategies through Google’s Keyword Planner and Google Trends, you can build an effective SEO strategy that grows your organic reach and generates revenue.]]>
Keyword mapping like this can help you think of every page on your site in terms of “themes.” If you see a theme in your keyword map that does not yet have a URL, you can consider creating a new URL for it. By leveraging these powerful keyword research strategies through Google’s Keyword Planner and Google Trends, you can build an effective SEO strategy that grows your organic reach and generates revenue.]]>Greg is the founder and CEO of Stryde and a seasoned digital marketer who has worked with thousands of businesses, large and small, to generate more revenue via online marketing strategy and execution. Greg has written hundreds of blog posts as well as spoken at many events about online marketing strategy. You can follow Greg on Twitter and connect with him on LinkedIn.
Greg Shuey
Greg is the founder and CEO of Stryde and a seasoned digital marketer who has worked with thousands of businesses, large and small, to generate more revenue via online marketing strategy and execution. Greg has written hundreds of blog posts as well as spoken at many events about online marketing strategy. You can follow Greg on Twitter and connect with him on LinkedIn.
